OpenAI o1 and o1 mini: Advancing AI Reasoning
OpenAI's o1 and o1 mini showcase advanced reasoning capabilities in large language models, building upon research in learning to reason.
Recent discussions have highlighted several intriguing aspects of o1 and o1 mini:
o1 represents a significant shift in AI architecture and reasoning capabilities. It marks a move towards scaling adaptive compute at inference time, embodying an advanced "thinking before answering" approach. This architectural innovation is best understood by comparing it to traditional models.
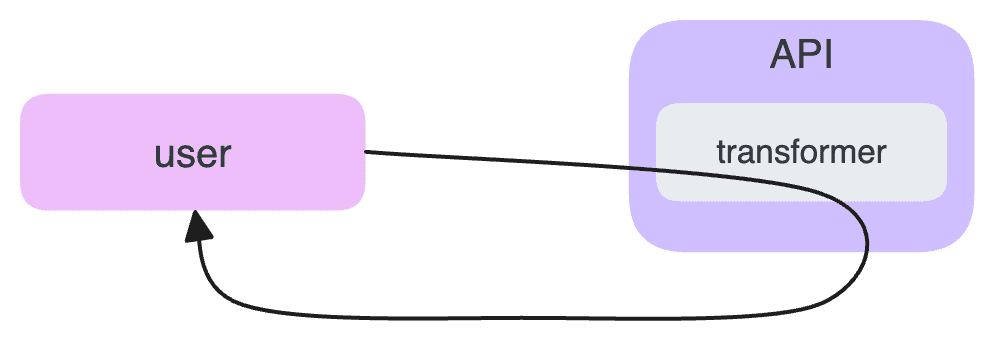
Traditionally, AI models like GPT have been transformer-based, with an API wrapping a single large language model. This approach, while powerful, has limitations in complex reasoning tasks.
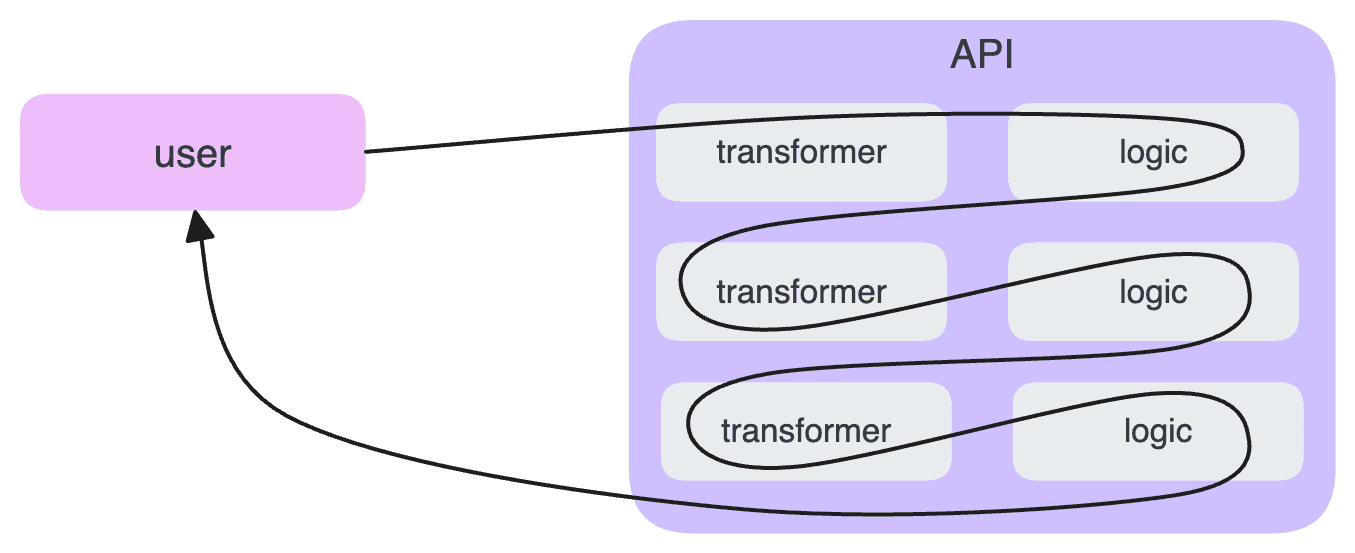
In contrast, o1 utilizes an agentic workflow behind its API. This means it can break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, much like a human would approach problem-solving. This architectural difference allows for more sophisticated reasoning and adaptability.
Specialized focus
o1 demonstrates a specialized focus on STEM-related tasks, particularly excelling in coding and technical problem-solving. This specialization is a result of its training, which heavily emphasized reasoning about STEM questions.
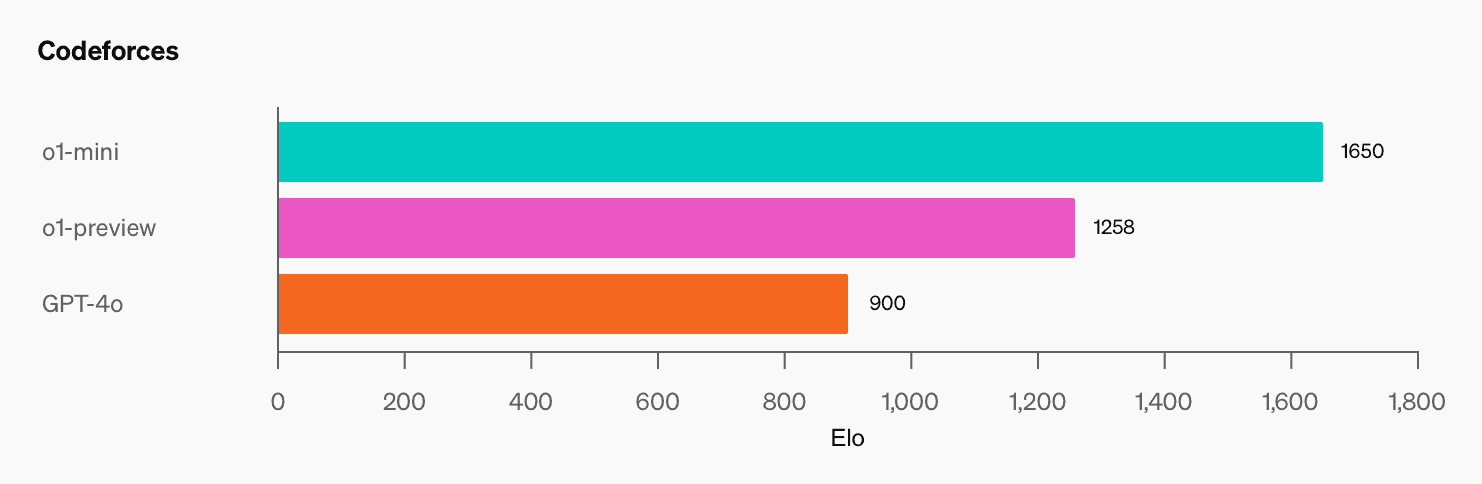
However, this specialized training comes with trade-offs. The model's exposure to literature, popular culture, and creative writing was comparatively limited. As a result, o1 may struggle with tasks requiring broader cultural knowledge or creative expression.
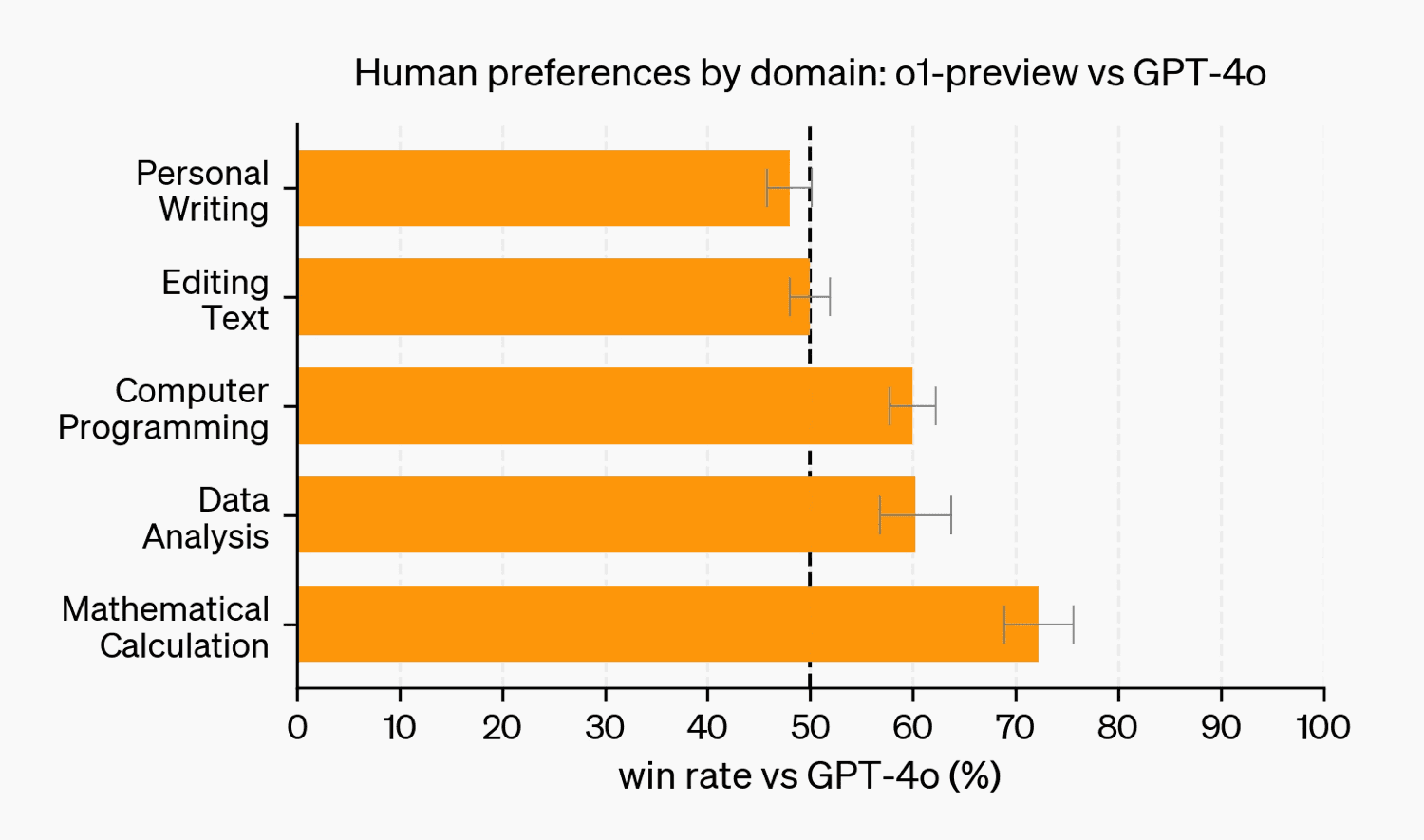
This specialization highlights an important consideration in AI development: the balance between depth in specific domains and breadth across diverse fields of knowledge. While o1 excels in its targeted areas, it may not be the optimal choice for tasks outside its primary focus.
Black box
While o1 offers advanced reasoning capabilities, its complex nature raises new questions. The black-box aspect of these models, combined with their intricate decision-making processes, introduces concerns about potential biases and logical fallacies that may be harder to detect and address.
Early observations suggest o1 excels at complex problem-solving but at higher costs, potentially best suited for high-level reasoning tasks. In contrast, o1 mini seems designed for integration into coding tools, with faster performance and a focus on coding problems.
Deconstructing complex tasks
These systems demonstrate the effectiveness of deconstructing complex tasks into simpler ones through agentic workflows. However, the cost implications are significant, with token costs for o1 being considerably higher than traditional models.
As the AI landscape evolves, we see a spectrum of tools balancing sophistication with accessibility and cost-effectiveness. The key will be choosing the right tool for each specific task.
For more in-depth discussions on these topics and others in AI development, please consider joining our Discord community, linked in the footer.